3.1 Basic Rules of Differentiation
Four Basic Rules of Differentiation:
1. Derivative of a Constant:
The derivative of a constant function is always equal to 0.
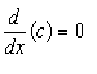
Proof:

2. The Power Rule
The derivative of a power function is equal to the exponent times the quantity of the variable raised to the power of the exponent minus 1.

Proof:
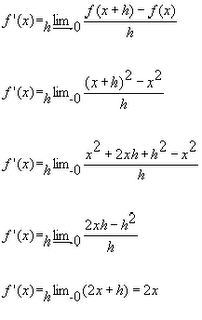
3. Derivative of a Constant Multiple of a Function
The derivative of a constant time a function is equal to the constant times the derivative of the function.

Proof:

4. The Sum Rule
The derivative of the sum or difference of 2 functions is equal to the sum or difference, respectively, of their derivatives.

Proof:

Example Problem:
Find the derivative of the function f by using the rules of differentiation.

Links to Derivatives:
http://archives.math.utk.edu/visual.calculus/2/index.html
http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Derivative.html
Brian, you're up next with 3.2 The Product and Quotient Rules
Derivative Joke:
Q: What is the first derivative of a cow?
A: Prime Rib!

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home